Some Cool Title
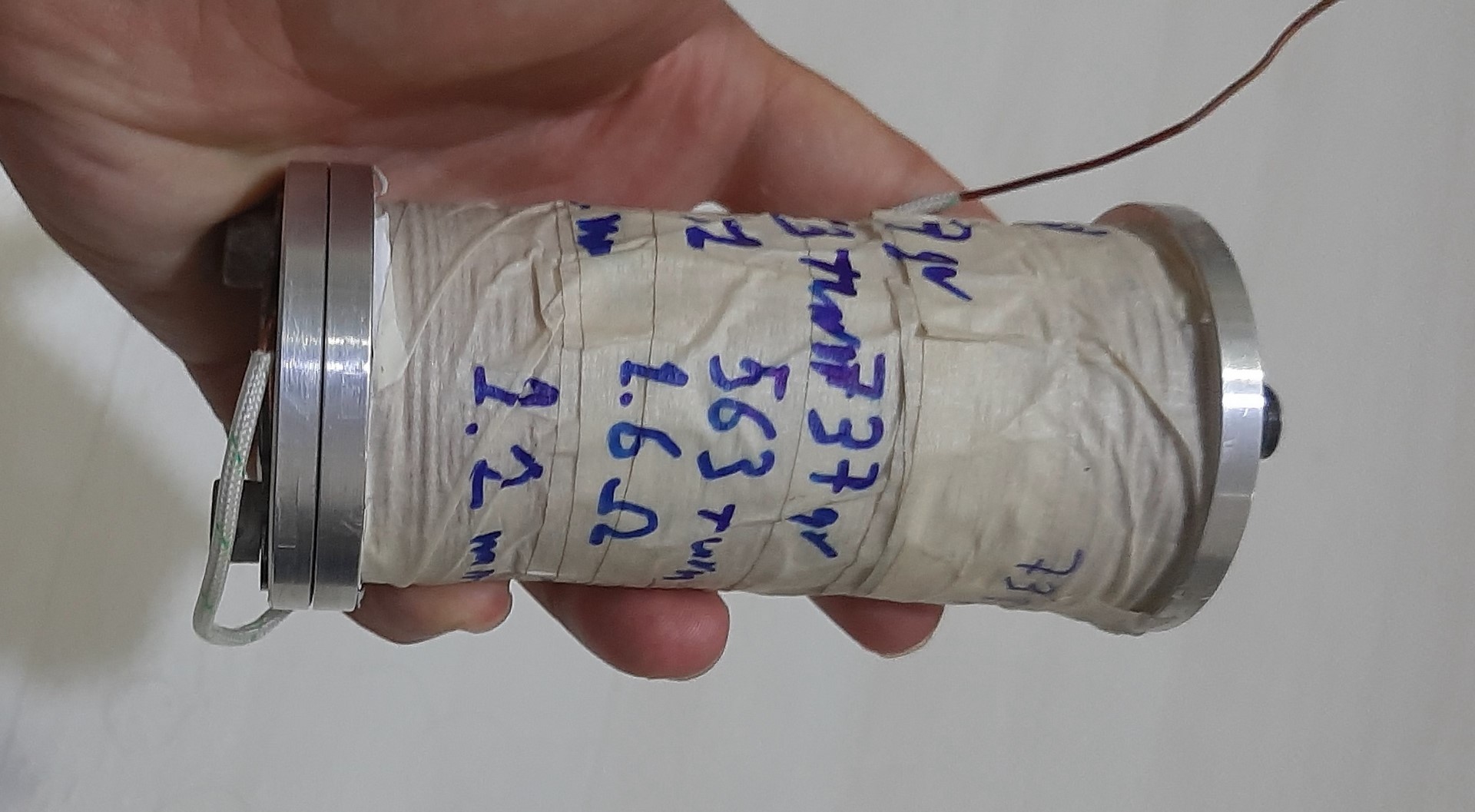
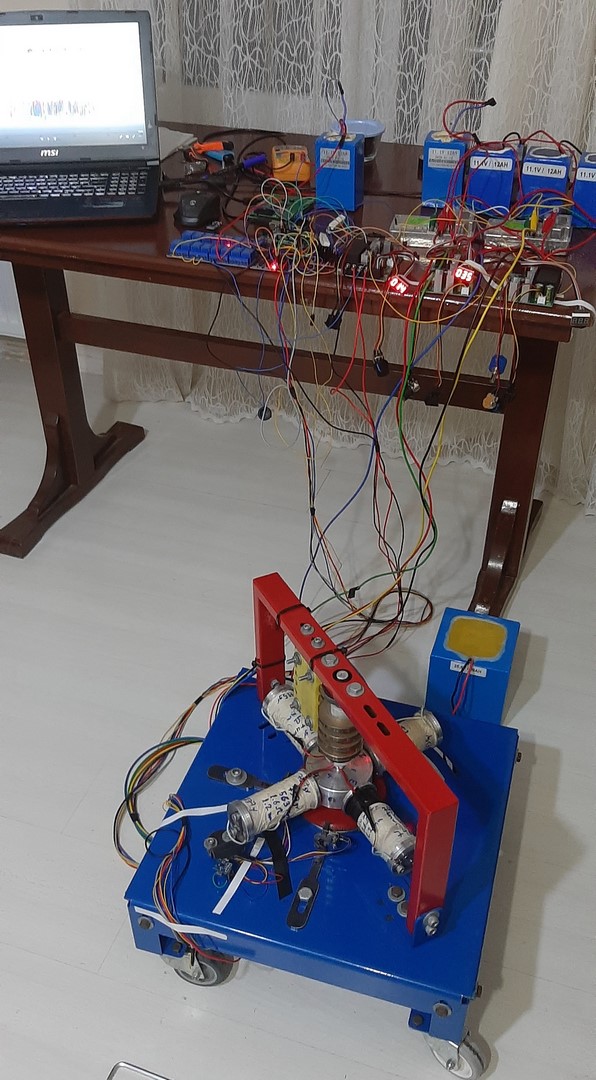
A radial electromagnetic actuator is shown in the figure below.

The system in the state in which 4 radial electromagnetic actuators are connected to the aluminum part is shown in the following figures.
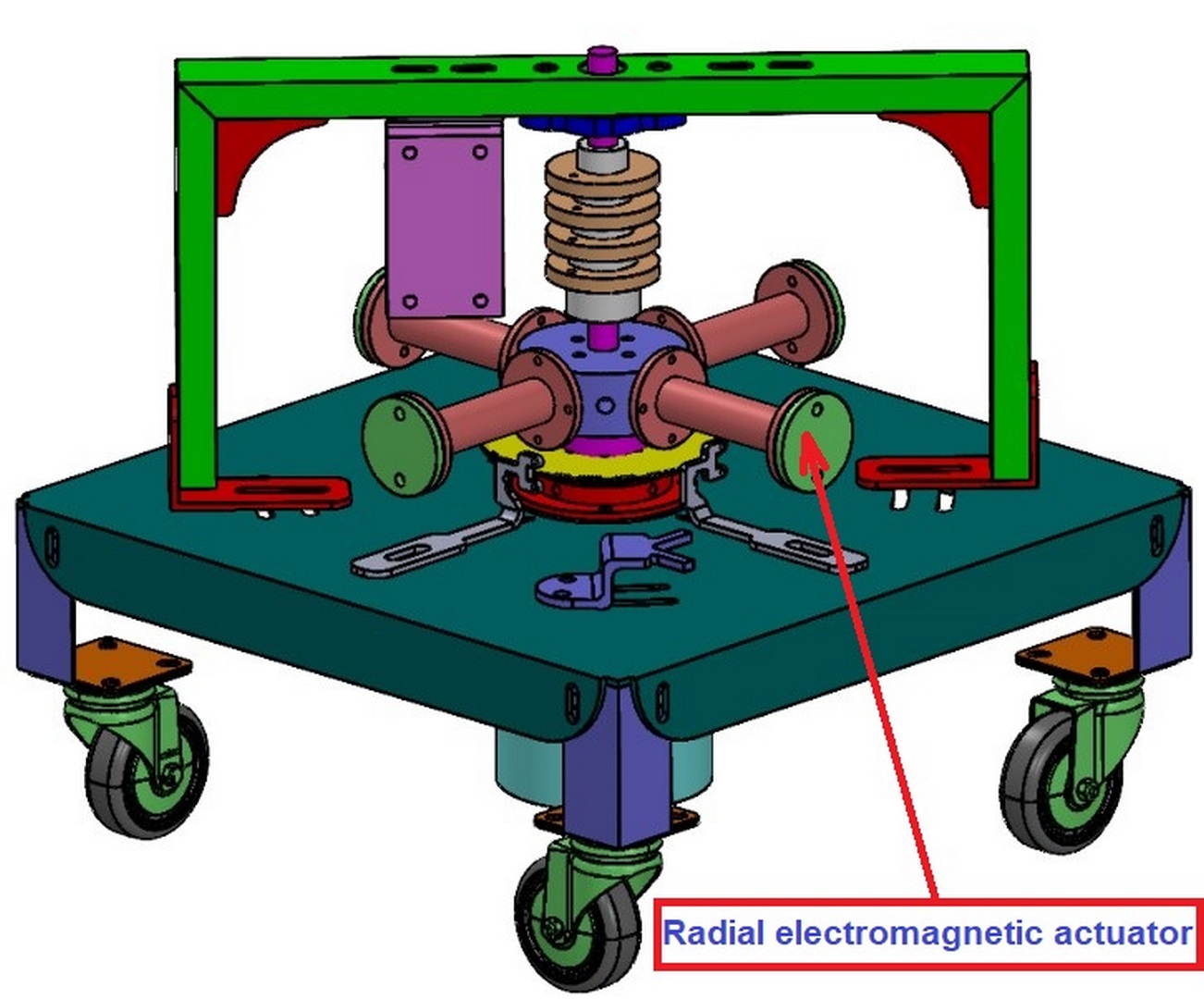
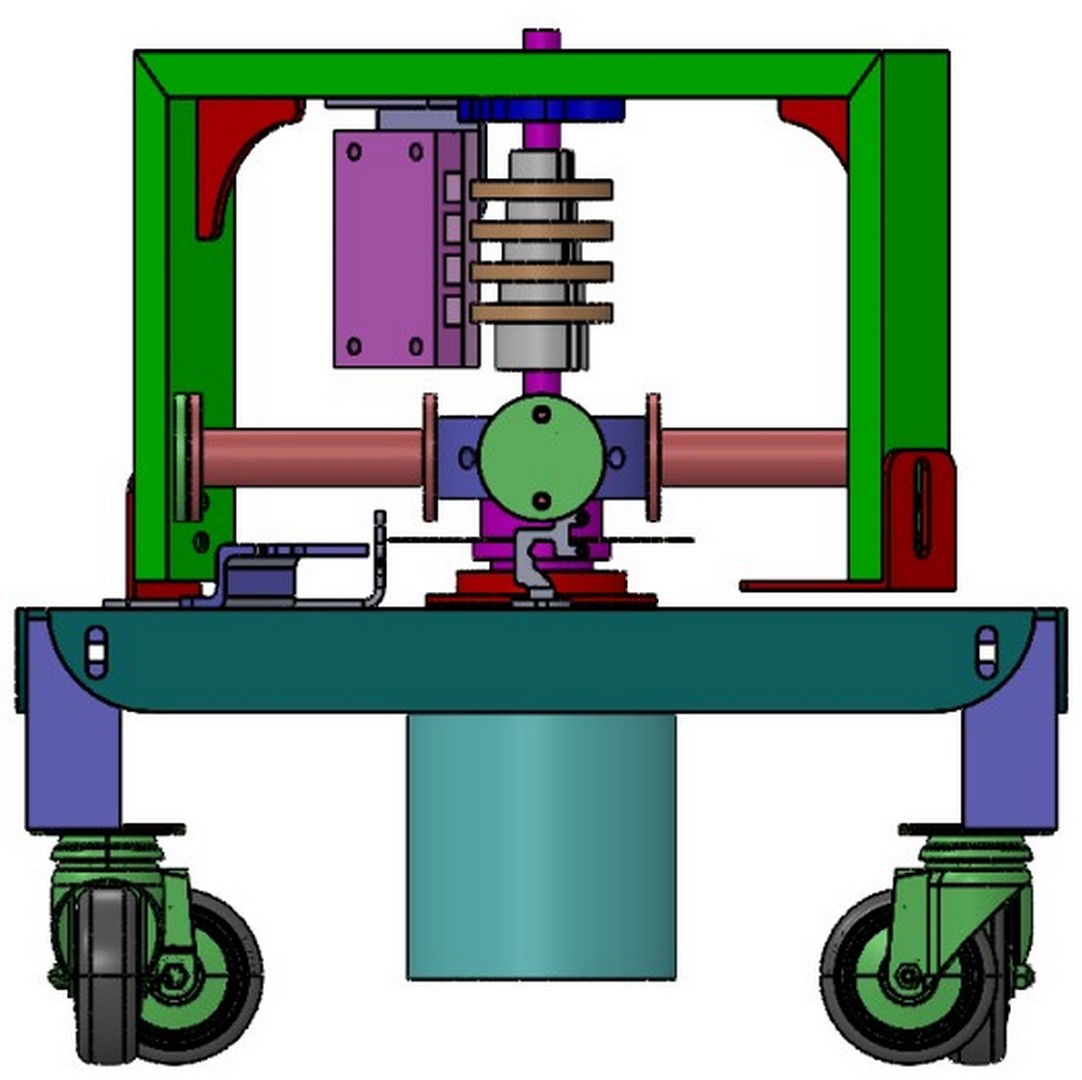

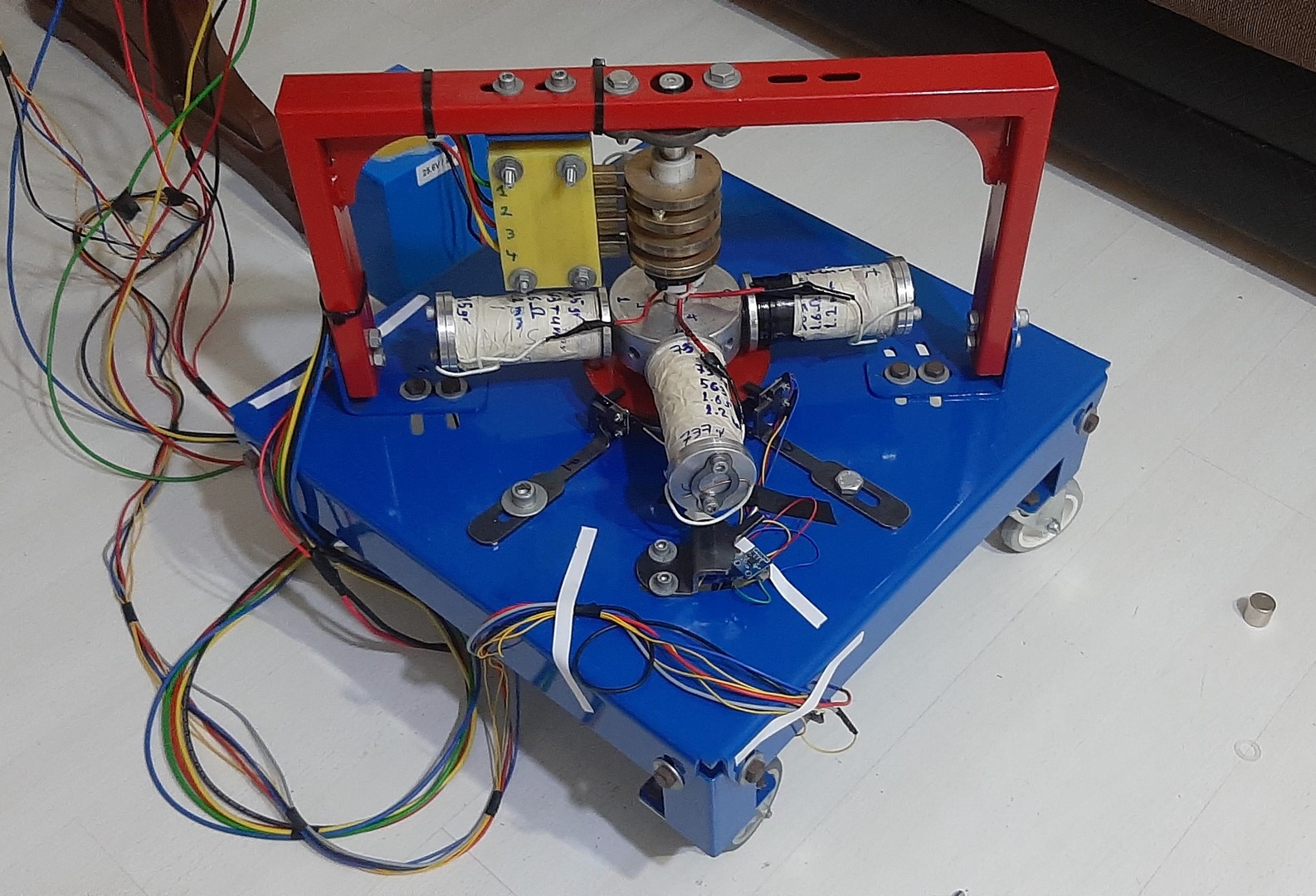
This system has interesting functional aspects. We can build the following elements into the core of an electromagnetic actuator:
- An iron cylinder
- A permanent magnet
- Two permanent magnets in a state in which the poles of the same name face each other
In each of the above cases, the system has a different functional behavior. If more accurate modules can be used to measure the acceleration caused by the system vibrations, we can balance the system to a considerable extent. The important point in this project, based on which I designed and implemented this project, is that if we have an accurate system to measure the acceleration and drive the actuators, we can use this type of radial electromagnetic actuator to generate a desired centrifugal force at any angle of rotation of the system. In other words, with this type of actuators, we can generate a desired centrifugal force in a cylindrical coordinate system at any angle.
In a sense, we can say that in this system, instead of generating a force in the X and Y directions, we can have a system that generates a force that depends on the magnitude of the force and the angle of rotation.
I have ideas in this regard, which I am researching and investigating. But the question arises as to what this kind of system is good for. In rotating systems where there is a variable dynamic unbalance in the system, be it a force dynamic unbalance (i.e. the amount of unbalanced mass changes) or a displacement dynamic unbalance (i.e. the unbalanced mass is constant but the mass changes relative to the rotational position at a different location) or both modes together, these types of actuators can be very suitable due to their short response time.
About 21 years ago, on December 26, 2003, there was a huge earthquake in the city of Bam in Iran, which unfortunately killed many people. At the time, I was a college student researching on a project that dealt with the resilience of dynamic and static structures. At that time, there were no testing facilities at universities to accurately test the dynamic resistance of structures. So I decided to design a seismic table that simulated the effects of an earthquake and then built it. I remember shortly after that project, I was invited by one of the universities in Australia to do a research project and I was there for a while. The main idea for the smart balance project with a variety of actuators also came from the same seismic table project in 2003.
The basic description and introduction of the system can be found in the following video.
The following video shows the performance of the system in radial electromagnetic actuator mode.